
05.04.24
Ozonated water for a clean and sustainable environment
The search for environmentally friendly and efficient cleaning solutions leads us to a technology that is already shaping the future of sustainable hygiene today. Ozonated water combines versatile use with ecological responsibility and opens up new perspectives for industry, healthcare and environmental protection. The ozonation of water represents a paradigm shift in cleaning technology that offers both economic and ecological advantages.
How does ozonated water work as a cleaning and sanitising agent?
Cleaning with ozonated water is a sanitation process that uses O₃. Ozone is a molecular compound consisting of three oxygen atoms (O₂O), in which two oxygen atoms come from the basic oxygen molecule (O₂O) and a third oxygen atom is contained that can be easily detached from the ozone compound and reattached to other molecules. When this third oxygen atom, also known as a radical, binds to the molecules of other substances, it can destroy their structure through oxidation.
Ozonisation is the infusion of ozone into water to both disinfect water and be used as a sanitiser for various applications and industries. During ozonisation, ozone acts as a highly reactive oxidising agent, directly attacking the surface layer of microorganisms and destroying their cell walls. When ozone is added to water, it quickly dissolves impurities without changing the composition of the water.
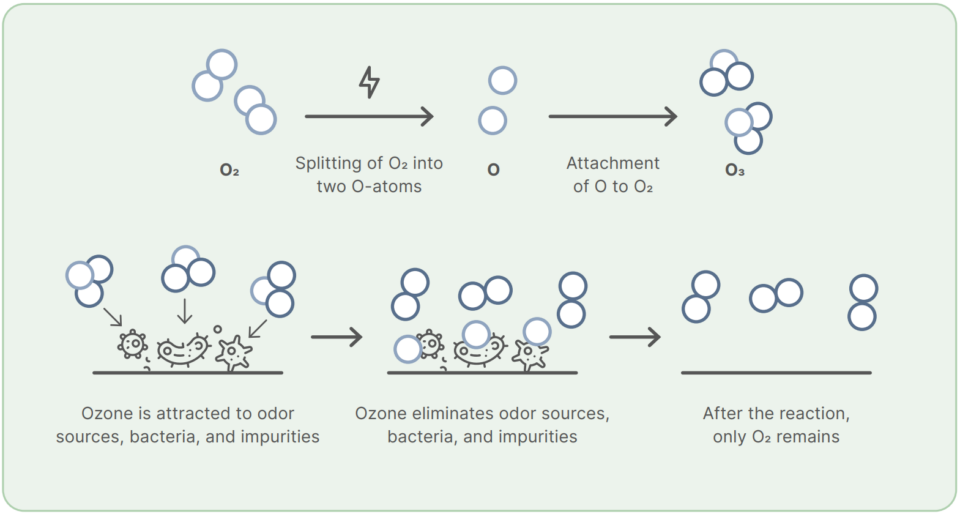
The special property of ozone is that it decomposes into pure oxygen after the reaction and leaves no harmful residues.
Current scientific developments show promising progress in various areas of application. New research findings in the wastewater treatment sector underscore the growing importance of this technology, especially in view of the increasing challenges posed by complex industrial wastewater.
How ozonated water is produced and how ozone water is revolutionising purification technology
In most cases, an ozone generator uses electrolysis to produce O3, which is bound in water to form ready-to-use ozonated water. Its oxidative effect effectively eliminates microorganisms, viruses and bacteria. The use of ozonated water in the food industry has shown impressive results in reducing germs. A meta-analysis shows that ozonated water achieves an average germ reduction of 1.65 ± 0.14 log when cleaning fresh food.
Significant progress has been made in the medical field. Recent studies on the treatment of pericoronitis demonstrate the antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties of ozonated water, opening up new perspectives for medical applications.
Ozone purification in various branches of industry
Ozone cleaning offers a sustainable solution for various industrial applications. The versatility of this technology is demonstrated by its successful implementation across different industries.
Floor cleaning and facility management
In professional building cleaning, ozonated water is increasingly being investigated as a complementary alternative to conventional cleaning agents. Studies and practical reports indicate that, under certain conditions of use, it can enable effective cleaning and reduce the consumption of traditional chemicals. Facility managers report lower costs and environmental benefits in this context, for example through reduced chemical consumption and lower transport and storage costs. However, the complete replacement of conventional cleaning chemicals has not yet been confirmed by reliable, comprehensive scientific data and depends heavily on the specific application.
Dry cleaning and laundries
Ozonated water is increasingly being used in commercial textile cleaning as a supplement to conventional washing processes. Various practical reports and technical studies show that the use of ozone can support cleaning performance and significantly reduce the need for traditional detergents. This is associated with potential savings in costs and resources, as well as ecological advantages due to the reduced use of chemical additives. However, the actual reduction depends on the respective system, water quality and specific washing processes.
Dishwashing in the catering industry
Ozonated rinsing systems can support cleaning performance in commercial dishwashers and significantly reduce the consumption of certain rinsing chemicals. Practical reports from the catering industry point to ecological advantages and potential cost savings, as fewer chemical additives and lower temperatures are required. However, the actual amount saved depends on the specific appliance system, water quality and operating conditions.
food processing
Ozonated water is increasingly being used in food processing as a complementary technology to reduce microbiological contamination and extend the shelf life of products. Studies show, for example, that on surfaces in fish processing and storage environments, mesophilic bacteria are reduced by approximately 48% and psychrophilic bacteria by approximately 37% immediately after treatment, and by up to approximately 80% and 99% after prolonged storage. Further analyses prove that ozone and ozonated water can also improve the quality and shelf life of fruit, vegetables and meat.
Ozone disinfection: an environmentally friendly alternative to chemicals
Ozone disinfection in water and wastewater treatment plants enables highly effective reduction of pathogens and leaves comparatively fewer chemical residues compared to some conventional methods. Studies describe ozone as a fast, broadly effective technology that leaves no harmful chemical residues.
Modern ozone purification systems and EU regulations
Modern ozone purification systems fall under Regulation (EU) No 528/2012 (BPR) for biocidal products in the European Union. In particular, ozone gas is subject to authorisation as an active substance for certain areas of application.
For the distribution of ozone generators or systems with ozone generation for biocidal use, manufacturers and distributors must provide evidence of effectiveness, safety and the application environment. Industry organisations such as EuOTA AISBL support manufacturers with information, consortium dossiers and access to active substance data.
Although the legal framework is in place and largely defined, “legal certainty” in specific cases depends on whether all national regulatory requirements have been met, the technical design has been documented, and the product has been approved accordingly. Companies should therefore check on a case-by-case basis whether their systems fully comply with the requirements.
Innovative developments and future prospects
Ozone biofiltration combines ozonation with biologically active filtration and is used in water treatment as an advanced technology for removing organic pollutants and reducing disinfection by-products. Studies show that this combined process enables stable and efficient treatment without leaving long-term chemical residues in the water.
Healthcare facilities are investigating the use of ozone for surface and room disinfection. Since ozone can be toxic when inhaled, these applications require strict safety measures and the precise determination of suitable concentrations in order to achieve effective disinfection with the lowest possible risk.
Modern ozone purification systems can also be supplemented with sensor technology and IoT-based controls. These technologies enable continuous monitoring of ozone concentrations and automatic adjustment of ozone production to the respective process conditions. This improves the efficiency and safety of the systems in practical operation.
Economic considerations and sustainability
The introduction of ozonated water can lead to savings in chemicals, energy and process costs in many applications. Various field reports cite shorter payback periods; however, actual cost-effectiveness depends heavily on the industry, operating procedures and the scope of the installation.
Sustainability benefits arise primarily from the reduced use of chemical cleaning agents, the lower impact on wastewater streams and the fact that ozone decomposes into oxygen without leaving any residue after the reaction. When used properly, this can offer both ecological and operational advantages. For companies wishing to support their sustainability goals, ozonated water can therefore be an attractive complementary technology, provided that safety and monitoring requirements are met.

